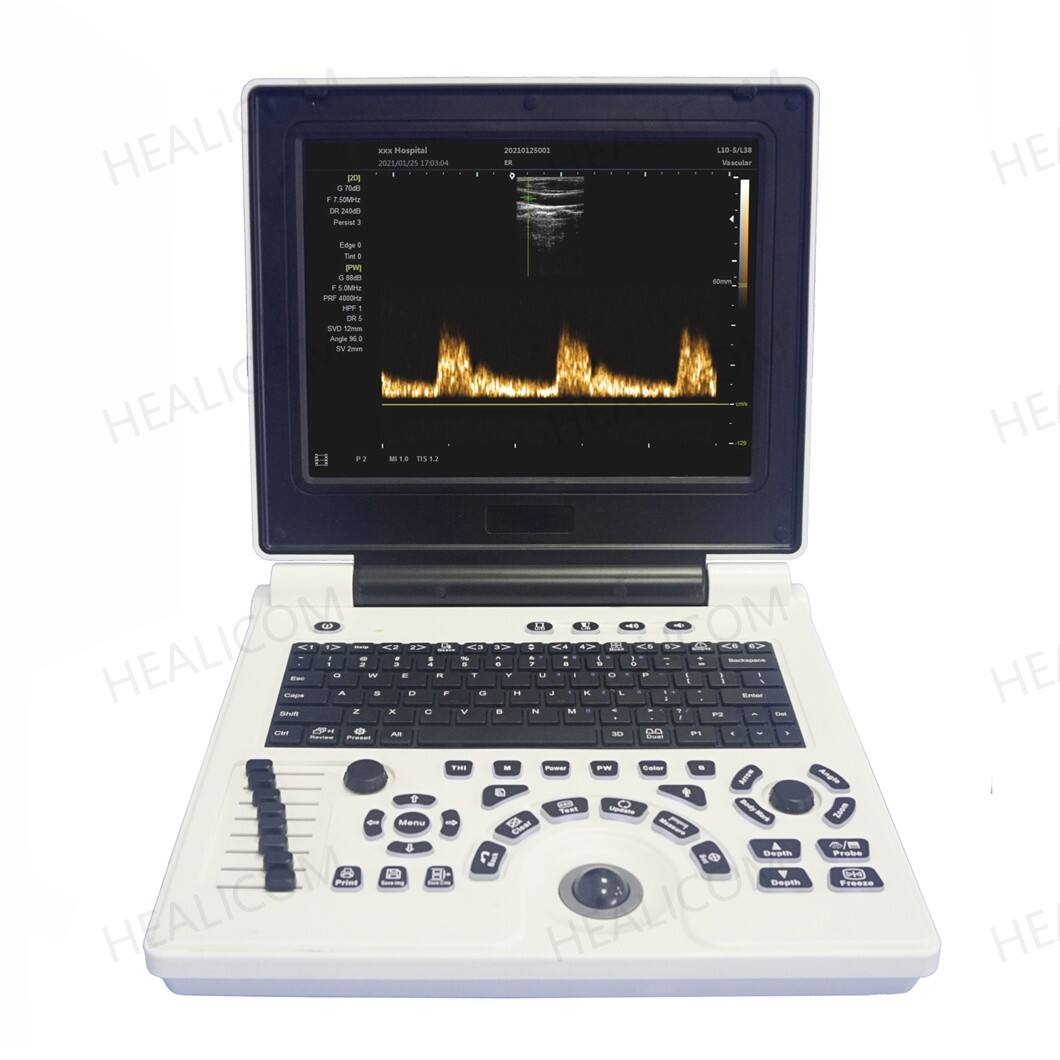
For modern portable ultrasound devices, getting good image quality is really important if doctors want to trust what they see at the patient's bedside. When images are sharp enough, medical staff can spot those tiny details in anatomy that matter so much. Think about finding little cysts or seeing problems with blood vessels before they become serious issues. That makes all the difference when someone comes in after an accident or needs quick evaluation while lying in bed. The best machines on the market today come with B-mode imaging which shows structures clearly, plus different types of Doppler technology like color flow mapping and pulsed wave analysis. These tools help track how blood moves through the body, something absolutely critical for checking heart health or spotting dangerous clots in leg veins that could travel to the lungs.
Real time elastography has really changed the game when it comes to looking at tissue stiffness. This tech helps doctors stage liver fibrosis and figure out what kind of breast lesions patients might have. But there's a catch. Getting good resolution while keeping those images coming fast enough (at least 30 frames per second) remains a challenge. If the system takes too long to process all that data, the images get delayed which isn't great during emergencies or urgent procedures. According to some research published last year, clinics in remote areas saw a boost in diagnostic accuracy around 35% when they used machines that combined dense scan lines with smart beamforming technology. That makes sense since many rural facilities don't have easy access for repeat scans. Most medical professionals prefer ultrasound equipment that offers two different settings one for detailed imaging and another for quick scans. These dual mode systems work well across various specialties including pregnancy monitoring, muscle and bone assessments, and even intensive care situations where speed matters most.
When working in places where resources are limited, the axial resolution matters a lot for making clinical decisions. Axial resolution basically means how well we can tell apart two points along the same line as the ultrasound beam. Devices that have around 0.3 mm or better resolution make it possible to spot the difference between complex cysts that aren't dangerous and actual solid tumors. But when using cheaper or older equipment with worse specs, these important differences might get lost. For FAST exams on trauma patients looking for free fluid in the abdomen, having at least 0.5 mm lateral resolution makes all the difference. We saw this confirmed in a big study last year across multiple emergency rooms where they tested six different portable ultrasound machines side by side.
The B-mode imaging technique serves as the base for most structural assessments, whereas pulse wave Doppler plays a key role when measuring how severe blockages are in carotid arteries. M-mode comes into play for tracking movements in real time, particularly useful for seeing how heart valves function during emergency situations. The newer 3D and 4D imaging features are starting to appear even in smaller portable devices now. But these advanced capabilities really only work well clinically if the image slices are thin enough under 2 millimeters thick and the system can rebuild images quickly enough to avoid those annoying motion artifacts that show up so often during fetal scans looking for abnormalities.
Shear-wave elastography now quantifies liver stiffness in kPa with 85% concordance against FibroScan® in NAFLD screening. Portable systems using AI-driven speckle reduction enhance real-time clarity by filtering noise without sacrificing frame rates—a feature shown to reduce scan-repeat rates by 50% in mobile ICUs according to a 2023 field trial.
Medical imaging devices equipped with single-button presets for routine examinations can boost workflow efficiency by around 22 percent when compared to traditional menu navigation systems. When it comes to quality assurance for ultrasound equipment, technicians focus heavily on checking contrast resolution which basically means how well the machine separates nearby soft tissue structures. This test usually involves running standard phantom models prior to actual patient scans. According to industry standards outlined in AAPM Report 274, any system showing more than an 8% difference in gray scale interpretation poses real risks. These discrepancies might lead to missed diagnoses of small but significant issues such as developing thyroid nodules at their earliest stages.
Portable ultrasound systems require transducer adaptability to meet diverse diagnostic needs.
The linear probes work really well for looking at blood vessels and muscles because they have those high frequencies that give good detail but don't go very deep into the body. For bigger areas like the belly or pregnant women's scans, doctors tend to reach for curvilinear arrays since these offer a much wider picture. Then there are those phased array transducers which squeeze through tight spots to get heart images, something absolutely critical during emergencies where quick ultrasound checks can save lives. According to recent studies from the Journal of Point of Care Ultrasound last year, medical staff actually make decisions 23 percent quicker when working with probes designed specifically for particular applications.
Handheld devices with dual-probe compatibility allow seamless switching between abdominal Doppler studies and cardiac assessments. For example, leading systems now support 85% of common clinical scenarios using just two interchangeable probes: a convex array for deep-tissue imaging and a linear transducer for superficial structures.
Modular probe designs reduce system weight by 40% compared to fixed-transducer units while maintaining diagnostic accuracy. Studies show clinics using interchangeable probes achieve 30% higher workflow efficiency in mobile settings by eliminating delays from device switching.
Invest in platforms supporting at least three probe types to accommodate emerging applications like lung ultrasound or procedural guidance. Prioritize systems with multi-probe compatibility to avoid costly upgrades as care protocols evolve—especially relevant given that 62% of healthcare facilities now use portable ultrasounds across four or more specialties.
Modern portable ultrasound systems emphasize integration with healthcare IT infrastructure through DICOM compliance, ensuring imaging data flows directly into electronic medical records (EMR). Research confirms that 88% of clinicians report improved diagnostic accuracy when ultrasound findings are embedded in unified patient records, reducing manual entry errors.
Using wireless transfer methods along with encrypted cloud storage makes it possible to share medical images securely between healthcare teams, all while staying compliant with HIPAA regulations. Take a small clinic out in the country for example. They can send abdominal scan images up to a major teaching hospital where specialists can look at them pretty much right away. Some research has actually found that this kind of fast access cuts down on waiting times for referrals by around 30-35%. That's a big deal when patients need timely diagnosis and treatment.
Portable systems with native DICOM support streamline workflows by automating image labeling and measurement documentation. This interoperability reduces redundant data entry by an average of 12 minutes per exam (Journal of Diagnostic Imaging, 2023).
Advanced devices offer dual-connection options: Wi-Fi for high-speed DICOM transfers and 5G cellular backup in remote areas. Cloud-based dashboards allow radiologists to prioritize critical cases, with some systems sending SMS alerts for urgent findings.
Integrated telemedicine platforms let less-experienced operators stream live scans to specialists. During a 2023 pilot in Alaska, this feature increased first-attempt diagnostic success rates from 62% to 89% in trauma assessments.
On-device AI algorithms provide automated measurements for cardiac ejection fractions and fetal biometry. In deep vein thrombosis triage, these tools reduce false negatives by 27% compared to unaided visual assessment (Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology, 2024).
Forward-looking systems include API access for third-party AI tools and telehealth plugins, creating modular platforms that evolve with healthcare networks. This flexibility future-proofs investments amid telemedicine adoption growing at 19% CAGR through 2030 (Global Market Insights).
 Hot News
Hot News